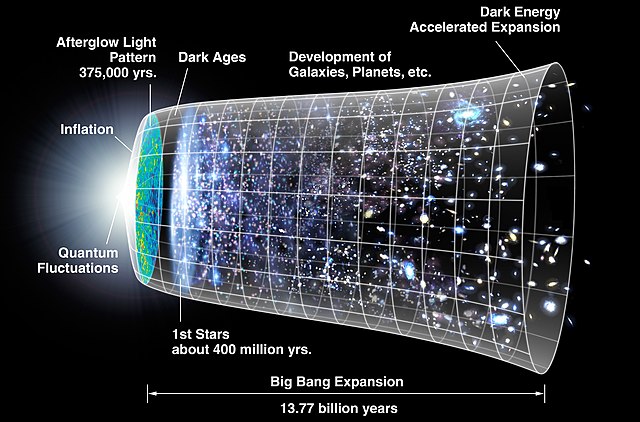
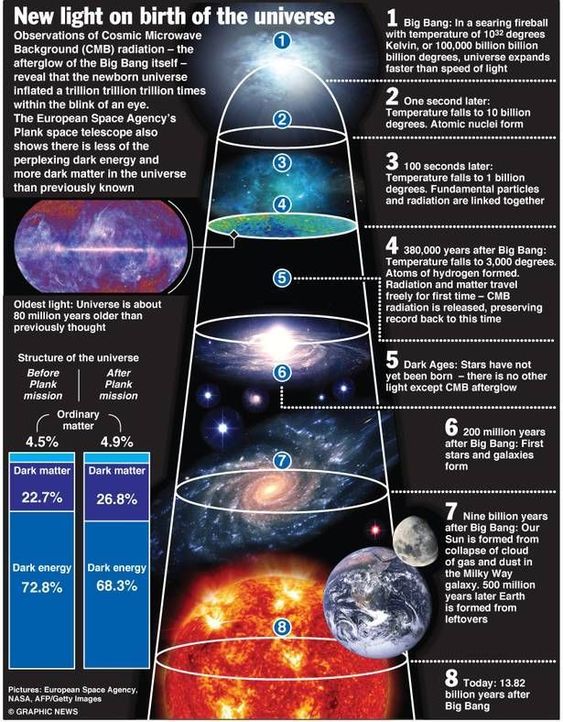
What is the origin of the universe? This is the ultimate origin question. The Big Bang is the scientific theory that proposes to answer this ultimate origin question. According to the Big Bang theory, the observable universe began in a singularity of infinite density and temperature at a specific moment in time some 13.8 billion years ago. It then rapidly expanded in to the vase and complex structure that we see today. The Big Bang theory has revolutionized our understanding of the universe by providing us with a framework to explain the origin and evolution of everything we see around us.
Deconstructing the Problem of the Origin of the Universe
The origin of the universe has been a topic of human interest since the beginning of recorded history and was likely discussed and debated from the time that language evolved. Only recently have we been able to make significant progress in outlining a theory of the origin of the universe grounded in observable evidence. This is mainly due to the fact that up until the last century scientists had limited observable evidence in which to accurately account for the universe’s beginnings. Powerful telescopes and other advanced instruments allowed scientists to learn more information about the universe’s structure, composition, and history.
In the early 20th century there were two main competing theory’s of the origin of the universe. The first and most popular was the steady-state theory, which postulated that the universe had no beginning or end and that it was in a state of perpetual equilibrium. The second was the expanding universe theory, which eventually became to be known as the Big Bang, postulated that the universe began as an incredibly hot and dense point, a singularity, and has been expanding and cooling ever since. As you can see, these are two very different views of the universe’s evolution. Eventually, some key lines of evidence began to emerge that settled the debate, leaving only the Big Bang theory left standing.
Key Lines of Evidence for the Big Bang Theory
There are three convincing lines of evidence typically put forward as proof for the Big Bang Theory. When all there of these are taking together it provides a compelling validation for the Big Bang Theory.
- Universal expansion of galaxies – this refers to the observation that all of the galaxies are moving away from each other, with the furthest galaxies moving a way at an accelerating rate. This phenomenon was first discovered by the astronomer Edwin Hubble in the 1920s when he observed that light from distant galaxies always shifted towards the red end of the spectrum. This line of evidence taken by itself does not prove the big bang. There could be a center far away where new matter is being created and ejected from the center, pushing everything away.
- Cosmic background microwave radiation – Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, while working on a satellite at Bell Labs, accidentally discovered the cosmic background radiation (CMB). The CMB is a form of electromagnetic radiation that fills the universe and is detectable in all directions, and is believed to be the residual heat left over from the Big Bang. It has a mostly uniform temperature of approximately 2.7 Kelvin, however small variations in temperature have been studied to provide important insights in the early universe, such as the distribution of matter and the structure of galaxies.
- Relative amount of light elements in the universe – The first few minutes of the early universe provided for extremely hot and dense conditions, with temperatures of billions of degrees and densities of billions of particles per cubic centimeter. The universe quickly expanded and cooled, allowing for nuclear fusion to occur, and the protons and neutrons that made up the early universe began to combine to form the lightest elements in a process called the Big Bang nucleosynthesis. The observed ratios of light elements such as hydrogen, helium, and lithium strongly match up with predictions made by the Big Bang.
Along with these three key lines of evidence there are other pieces of evidence that strongly support the Big Bang theory. The large scale structure of the universe and the age of the universe are both consistent with the predictions of the theory. Taken together, these lines of evidence provide strong support for the Big Bang theory, making it the most plausible explanation for the origin and evolution of the universe.
Continue reading more about the exciting history of science!